Understanding Pitted Keratolysis: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
We often take our feet for granted, until something causes discomfort, pain, or embarrassment. Pitted keratolysis is one such condition that can affect our daily lives. Understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatments can help us maintain healthy feet and prevent this bacterial infection from taking away our confidence and comfort.
Key Takeaways
- Pitted Keratolysis is a bacterial skin infection affecting the soles of feet and palms, characterized by small holes or pits in the skin.
- Risk factors include prolonged shoe-wearing and exposure to moisture, with healthcare workers, athletes and military personnel at increased risk.
- Prevention strategies such as maintaining foot hygiene & selecting appropriate footwear can reduce the chances of developing pitted keratolysis.
What is pitted keratolysis?
Pitted keratolysis is a bacterial skin infection. It mainly occurs on the soles of the feet and palms of the hands. Men are more likely to experience this condition, which can lead to soreness, itching, and even smelly feet. Though it might sound intimidating, pitted keratolysis can be treated and managed with proper care and attention.
Before discussing the treatment options, it’s necessary to understand the characteristic features of this skin disorder.
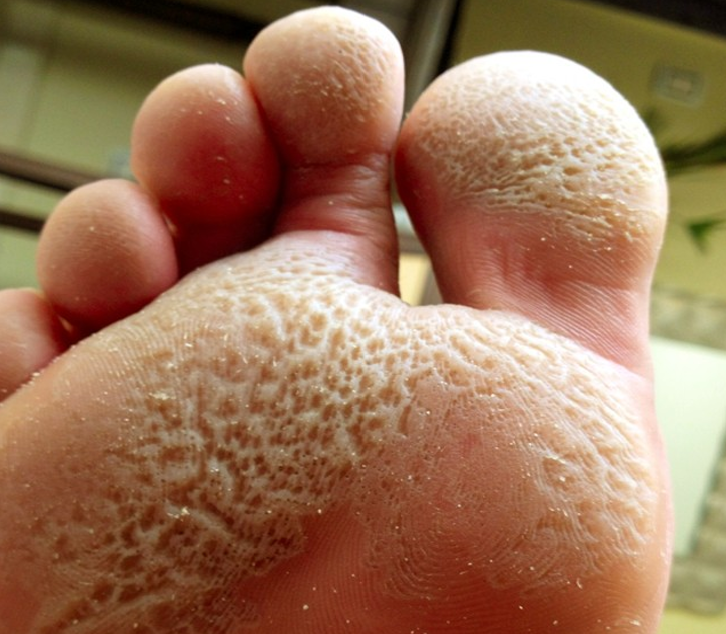
Appearance and Affected Areas
The tell-tale sign of pitted keratolysis is the presence of small holes or pits in the skin, which typically appear on the soles of the feet or palms of the hands. These pits may have a brownish hue and often become more visible when the feet are moist.
In some cases, patients may experience tenderness, itching, and a burning sensation in the affected areas. Recognizing these symptoms at an early stage is beneficial, as quick medical attention can hinder the condition from escalating, thus preventing further discomfort.
Variations and Severity
Pitted keratolysis, also known as plantar pitted keratolysis, has several variations, including:
- Keratoma plantar
- Keratolysis sulcata
- Keratolysis plantare sulcatum
- Ringed keratolysis
These variations can lead to smelly feet, which can be embarrassing and uncomfortable for those affected. The severity of pitted keratolysis can range from mild to severe, with larger lesions sometimes forming and joining together, especially in weight-bearing areas. This condition can also contribute to foot odour.
Early detection and treatment can help prevent further complications and alleviate the unpleasant symptoms associated with this condition.
Causes of Pitted Keratolysis
Pitted keratolysis is primarily caused by various bacterial species that thrive in moist conditions. Environmental factors, moisture, and certain occupations or risk factors can increase an individual’s susceptibility to developing this skin infection.
Comprehending the underlying causes of pitted keratolysis equips us with the knowledge to implement preventative measures and uphold skin health.
Bacterial infection
Several bacterial species are responsible for pitted keratolysis, including:
- Corynebacteria
- Dermatophilus congolensis
- Kytococcus sedentarius
- Actinomyces
- Streptomyces
These bacteria secrete proteinase enzymes, which degrade the keratin proteins in the stratum corneum, leading to the formation of characteristic pits and potentially involving sulfur compounds.
An accurate diagnosis and proper treatment are critical in preventing the condition from escalating and avoiding misdiagnosis-related complications, such as mistaking it for a fungal infection.
Moisture
Warm and moist environments, excessive sweating, and wearing tight-fitting shoes can increase the likelihood of developing pitted keratolysis. The bacteria responsible for pitted keratolysis prefer these conditions, making individuals with hyperhidrosis or living in a humid climate more susceptible to the infection.
Managing moisture and environmental factors effectively can significantly minimize the risk of contracting this skin infection. Implementing advanced skin wound care practices can also contribute to better outcomes.
Risk factors and occupations
Certain occupations that involve extended periods of wearing shoes are at risk for pitted keratolysis. Prolonged shoe-wearing and exposure to moisture can create an environment conducive to the growth of bacteria, leading to the development of the condition. Healthcare workers, athletes, and military personnel are among those at heightened risk of developing pitted keratolysis.
Individuals in these occupations can mitigate their chances of developing this skin infection by staying informed about these risk factors and managing them proactively.
Diagnosing Pitted Keratolysis
Diagnosis of pitted keratolysis involves several steps, including physical examination, skin scraping, and additional investigative methods if necessary. Once pitted keratolysis is diagnosed, an accurate diagnosis plays a crucial role in ensuring that the correct medications and interventions are prescribed to treat the infection.
Physical Examination
During a physical examination, doctors often diagnose pitted keratolysis based on its appearance and odour. Visual inspection of the affected areas, such as the feet, helps to determine the presence of characteristic pitted lesions.
Any associated odour should also be evaluated during the examination, as this can provide further insight into the severity and progression of the condition.
Skin scraping and microscopic analysis
To confirm the presence of bacteria responsible for pitted keratolysis, a skin scraping may be conducted. This procedure involves taking a sample of skin to analyze under a microscope for bacteria and parasites.
Microscopic analysis can accurately diagnose the condition and distinguish it from other skin disorders, such as fungal infections.
Additional investigative methods
In some cases, further investigations may be required to rule out other skin conditions. The following diagnostic tests may be recommended:
- Swabbing the affected area
- Performing a skin-scraping procedure
- Gram’s stain
- Culture studies
- Wood’s ultraviolet light examination
- Histopathology
These tests can accurately identify the type of bacterial infection causing the issue and determine the severity of the condition.
Pitted Keratolysis Treatment Options
Treatment options for pitted keratolysis include topical antibiotics, foot care, and advanced treatments in severe cases. By adhering to a prescribed treatment plan and implementing necessary lifestyle changes, individuals can have their pitted keratolysis treated, alleviate the symptoms, and avert its recurrence.
Topical Antibiotics and Antiseptics
Topical antibiotics and antiseptics, such as clindamycin, erythromycin, or mupirocin, are commonly used to treat pitted keratolysis. These medications are applied directly to the affected skin, typically twice daily for up to two weeks. While topical antibiotics are generally effective in treating pitted keratolysis, they may cause side effects such as skin irritation, redness, and itching. In rare cases, an allergic reaction may occur.
Lifestyle Changes and Foot Care
Maintaining good foot hygiene, effective moisture management, and refraining from wearing tight-fitting footwear are crucial in treating pitted keratolysis. Keeping the feet dry, washing them frequently with antiseptic cleanser, and wearing moisture-wicking socks can help prevent the condition from recurring.
Additionally, choosing open-toed sandals and wearing shoes for as little time as possible can reduce the risk of developing the infection.
Advanced Treatments
In extreme cases, treatments like botulinum toxin (Botox) injections may be recommended. These injections can help manage excessive sweating, a contributing factor to the development of pitted keratolysis. However, it’s paramount to consult with a healthcare professional before considering advanced treatments, as they may not be suitable for everyone and could carry potential side effects.
How to prevent pitted keratolysis
Preventing pitted keratolysis involves maintaining foot hygiene, avoiding the use of occlusive footwear, selecting appropriate footwear, and avoiding shared footwear.
Taking proactive steps to maintain clean, dry, and well-cared-for feet can lower the risk of developing this bacterial skin infection, leading to healthier, happier feet.
Foot Hygiene and Moisture Management
Maintaining dry feet, washing them regularly with an antiseptic cleanser, and using moisture-wicking socks can aid in preventing pitted keratolysis. It’s also essential to change socks regularly, especially after exercise or exposure to moisture, to maintain a dry environment that discourages bacterial growth.
Footwear Selection and Alternatives
To reduce the risk of pitted keratolysis, choose breathable footwear that allows adequate ventilation and keeps the feet dry. Ensure that shoes are properly fitted and not too tight, as tight footwear can create a moist environment conducive to bacterial growth.
Opt for open-toed sandals when possible and avoid wearing occlusive footwear for extended periods to promote airflow around the feet.
Avoiding Shared Footwear
Sharing footwear can increase the risk of spreading pitted keratolysis between individuals. To prevent the spread of this skin infection, wear your own shoes and refrain from sharing them with others.
Upholding personal hygiene and refraining from sharing footwear can safeguard us and others from the discomfort and inconvenience caused by pitted keratolysis.
Conclusion
In conclusion, pitted keratolysis is a bacterial skin infection that can be both uncomfortable and embarrassing. By understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatments, you can take proactive measures to maintain healthy feet and prevent the condition from affecting your daily lives.
Remember that proper foot hygiene, moisture management, and appropriate footwear selection are crucial to preventing and treating pitted keratolysis. Keep your feet clean, dry, and well-cared for to enjoy a happier, healthier life. If you suspect that you have pitted keratolysis on your feet, book an appointment with us so we can inspect your feet and diagnose your condition. We’ll also provide you with a treatment plan to help you heal from this skin condition.